Undervolting a GPU involves reducing the voltage supplied to the graphics processing unit while maintaining stable performance. This process has gained traction among tech enthusiasts as a way to optimize a GPU’s power consumption without sacrificing performance. Let’s delve into the step-by-step guide to understanding undervolting and its benefits:
Understanding GPU Voltage
Voltage supplied to a GPU determines its power consumption and heat generation. Traditionally, GPUs are supplied with higher voltages than necessary for stable operation to ensure reliability across different chips.
Potential Benefits of Undervolting
Undervolting aims to find the lowest stable voltage for the GPU. This process can lead to several advantages:
- Reduced Power Consumption: Lowering voltage decreases power draw, leading to energy savings.
- Lower Heat Generation: With reduced voltage, the GPU generates less heat, potentially improving overall system temperature.
- Extended Lifespan: By running at lower voltages, the GPU experiences less stress, potentially prolonging its lifespan.
Tools for Undervolting
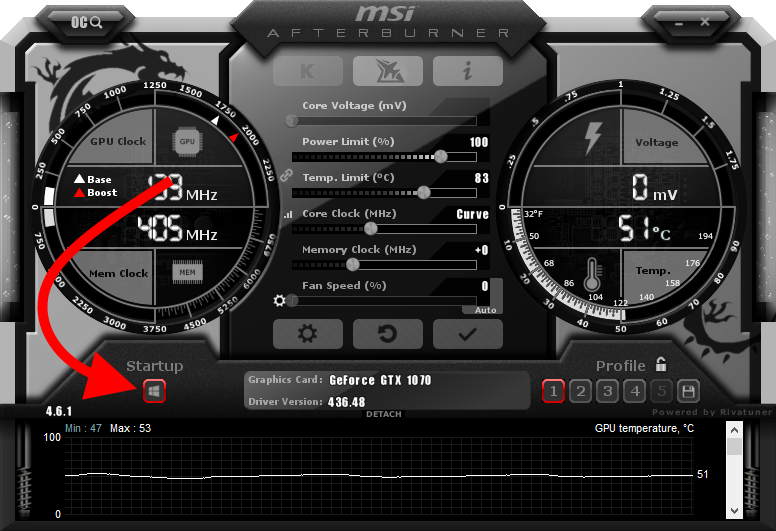
Various software tools, depending on your GPU manufacturer, allow adjustment of voltage settings. AMD GPUs commonly use software like MSI Afterburner or Radeon WattMan, while NVIDIA GPUs utilize tools like MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X.
Baseline Performance Metrics
Before undervolting, establish baseline performance metrics. Run benchmark tests or monitor GPU performance using software like MSI Afterburner to note the default voltage, temperature, and performance under load.
Gradual Voltage Reduction
Access the GPU tuning software and begin the undervolting process. Start by slightly decreasing the voltage in small increments (e.g., -10mV) and testing for stability. Run stress tests or benchmarks to ensure the GPU remains stable without crashing or artifacts.
Stability Testing
After each voltage adjustment, stress test the GPU using applications like FurMark or 3DMark to check for stability. If the GPU remains stable without issues, proceed with further voltage reduction.
Monitoring Temperature and Performance
Continuously monitor the GPU temperature and performance while undervolting. Ensure that the temperature remains within safe limits and that performance doesn’t degrade significantly. Adjust the voltage if needed to maintain stability.
Finding Optimal Settings
Continue adjusting voltage settings incrementally until you find the lowest stable voltage that maintains optimal performance without compromising stability or causing crashes.
Save Settings and Apply
Once you find the optimal undervolted settings, save them within the GPU tuning software. Apply these settings to ensure they are active whenever the GPU operates.
Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
Regularly monitor the GPU’s performance and temperature after undervolting. It might be necessary to make occasional adjustments to maintain stability as system updates or environmental conditions change.
Final Thought:
Undervolting a GPU offers a balance between power efficiency, temperature reduction, and potential performance improvements. Through careful adjustments and testing, users can optimize their GPU’s voltage settings, reducing power consumption and heat generation while maintaining stable performance. However, it’s essential to proceed cautiously and monitor the GPU’s behavior throughout the undervolting process to ensure stability and optimal performance.