Like air coolers, liquid coolers cool the internal components of a computer using the basic principle of thermodynamics – heat is transferred from a hot object to a cold object. Liquid cooling is a very common practice, but the method of operation is still confusing to many who believe that water destroys electronics when they are in direct contact.
In this article, we will discuss the principle of operation of a liquid CPU cooler, why liquid cooling is better than air cooling, and the components of a liquid CPU cooler.
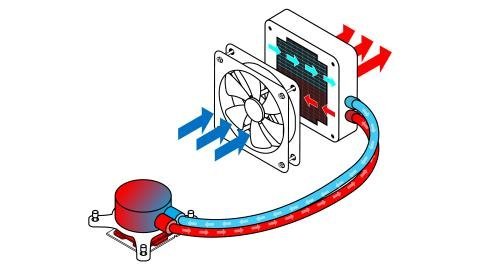
How it works?
You may wonder why liquid cooling is recommended when it is well known that liquid should not come in direct contact with electronic components. The liquid cooling process does not require direct contact between the liquid and the electronic components.
Liquid CPU coolers use a heat-conductive metal called water blocks that are filled with hollow tubes and channels through which liquid coolant flows. The base of the water block is placed directly on top of the electronic components, and the thermal paste between the two surfaces guarantees better heat transfer.
When electronic components heat up due to heavy loads, it heats the surface of the water block. As the liquid coolant flows through the channels and tubes in the water block, it absorbs heat from the metal base of the water block, which cools the metal and electronic components.
Liquid coolant moves through channels and then up a tube until it reaches the radiator. The radiator exposes the liquid coolant to cold air, which cools the liquid coolant. The radiator fans then move the heat away from the liquid cooler. The liquid coolant, now cold, re-enters the water block and starts the cooling cycle again.
Why is liquid cooling better than air cooling?
Here are the reasons why you should consider liquid cooling over air cooling.
This is a more efficient cooling process
Excessive heat in the computer’s internal components can overwhelm the air-cooling system, causing the fans to run at maximum speed. Liquid cooling uses water or other fluids as its coolant. Because water has a higher thermal conductivity than air, it can absorb more heat and cool the computer faster.
If your computer generates more heat than it absorbs air, it may overheat. Liquid cooling is more effective at cooling computer systems that generate a lot of internal heat.
It reduces noise
When you run power-intensive programs on your computer, it generates a lot of heat that requires a lot of cooling. If you are using an air cooler, your fans will run at maximum speed to draw enough air to cool the system. Fans make a lot of noise when your system runs powerful programs.
Liquid cooling systems produce less noise because water is better at removing heat from your computer’s internal components than air.
It reduces power consumption
Cooling a system is usually a chain reaction. First, running power-intensive programs on your computer heats up the internal components. Because too much heat can damage your computer, the cooling system is designed to dissipate heat.
More electricity is used because the fans run faster to cool the excess heat. Since an air cooler requires more effort to cool the computer, using a liquid cooler guarantees a reduction in power consumption
No dust build-up
One of the disadvantages of air cooling is that after a while the air filter becomes dusty. There are impurities in the air that the air filter prevents from being absorbed into the components through the vents. After a while, dust accumulates in the filter and blocks the air passage.
If you are using an air cooler, check and clean the air filter regularly. Since liquid cooling does not depend on airflow, it is not affected by dust accumulation.
Liquid CPU Cooler Components
Here are the parts for a liquid CPU cooler.
The pump
The pump is an integral part of the cooling process as it controls the speed at which liquid coolant flows through the tubes and channels.
When the pump draws liquid coolant from the coolant reservoir, it ensures that the coolant flow rate is not so fast that the liquid coolant does not have enough time to absorb heat from the computer components.
The pump also ensures that the coolant flow rate is not so slow that it accumulates too much heat on the internal components before it arrives and reaches the end of its cycle. Coolant cools the system when the flow rate is just right.
Radiator
After the coolant cools the metal base of the water block and the computer component, it travels through a tube to the radiator. At this time, the coolant is still hot. The radiator exposes the liquid coolant to cold air, removing heat from the coolant. The coolant then returns to restart the cooling process.
Water block
The water block is a barrier between the liquid coolant and the electronic components to prevent damage to the components. Its base is a heat-conducting metal, usually copper or aluminum, that absorbs heat from the component and transfers it to the coolant.
Liquid coolant
The coolant is usually distilled water. Distilled water is used because other types of water may contain impurities that can block the tubes or channels, preventing the passage of coolant.
Final Thought:
A liquid CPU cooler is a very common and effective tool for ensuring that your computer’s internal components stay cool even when running power-intensive programs. If you were worried about liquids causing damage to electronic components, you needn’t worry here due to the use of water blocks in liquid CPU coolers.