To test system performance, you may need to know the number of CPU threads running concurrently.
To make things easier for you, we have written a detailed step-by-step guide on how to check CPU threads in different ways.
What are threads in a CPU, and how do they work?
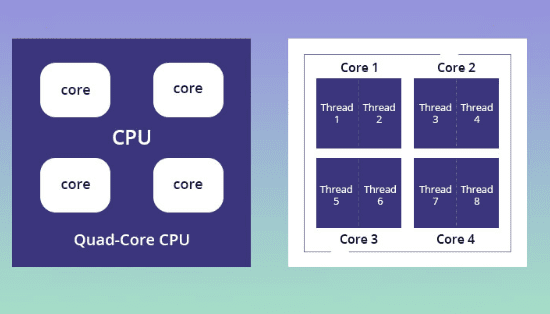
CPU threads are virtual codes that attach to physical computer codes, such as the core, and work with them to efficiently run different programs or applications simultaneously.
A single CPU core consists of two threads. Similarly, an octa-core CPU will have 16 threads. But these numbers in the processor also vary depending on the model and generation of the system.
When you open an application, the operating system creates a primary line, which takes information or input from the user, creates a thread, and simultaneously transmits commands to it. After that, another thread is created on the second command, and tasks are allocated by other threads and then executed.
CPU threads are being checked.
If you’re wondering how to check CPU threads, our 5 step-by-step methods below will help you get through the process quickly.
Method 1: Using Task Manager
You can easily check CPU threads using Windows Task Manager as follows.
- Press the Ctrl + Alt + Del keys simultaneously on the keyboard and click on “Task Manager” from the pop-up window.
- Click on “Performance”.
- Click on “CPU”.
What Are Threads in the CPU, and How Do They Work?
CPU threads are the virtual codes associated with the physical computer codes, such as cores, and work with them to execute various programs or applications simultaneously efficiently.
A single CPU core consists of two threads. In the same way, an octa-core CPU will have 16 threads. But these numbers in a processor also vary depending on the model and generation of a system.
When you open an application, the operating system creates a primary line, which takes the information or input from the user, creates a thread, and transfers commands to it simultaneously. Then, another thread gets created on the other command, and tasks are allocated onward by other threads and then executed.
Checking CPU Threads
If you are wondering how to check CPU threads, our following 5 step-by-step methods will help you go through the whole process quickly.
Method #1: Using the Task Manager
You can conveniently check the CPU threads using the Windows Task Manager in the following way.
- Press the Ctrl + Alt + Del keys simultaneously on the keyboard and click “Task Manager” from the pop-up window.
- Click “Performance”.
- Click “CPU”.
What Are Threads in the CPU, and How Do They Work?
CPU threads are the virtual codes associated with the physical computer codes, such as cores, and work with them to execute various programs or applications simultaneously efficiently.
A single CPU core consists of two threads. In the same way, an octa-core CPU will have 16 threads. But these numbers in a processor also vary depending on the model and generation of a system.
When you open an application, the operating system creates a primary line, which takes the information or input from the user, creates a thread, and transfers commands to it simultaneously. Then, another thread gets created on the other command, and tasks are allocated onward by other threads and then executed.
Checking CPU Threads
If you are wondering how to check CPU threads, our following 5 step-by-step methods will help you go through the whole process quickly.
Method #1: Using the Task Manager
You can conveniently check the CPU threads using the Windows Task Manager in the following way.
- Press the Ctrl + Alt + Del keys simultaneously on the keyboard and click “Task Manager” from the pop-up window.
- Click “Performance”.
- Click “CPU”.
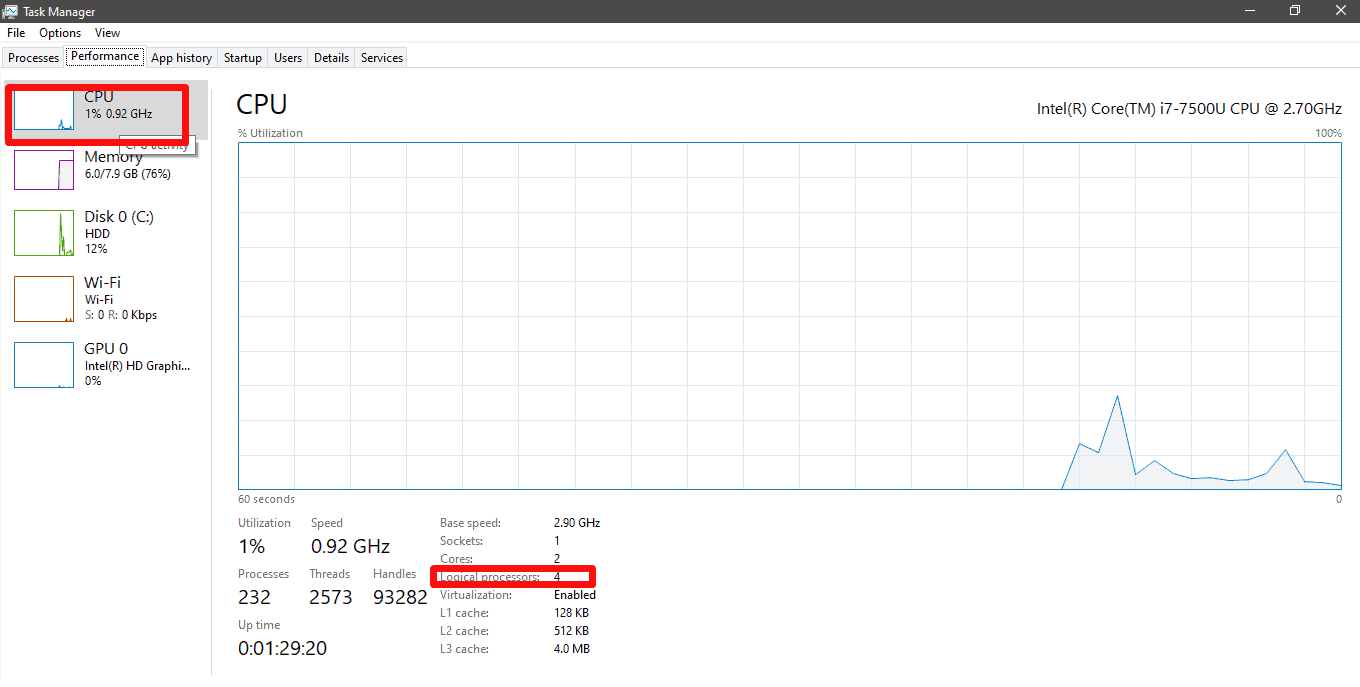
You will see the total number of CPU threads next to “Logical Processors”.
Method #2: Using Device Manager
After these steps, you can also get information about CPU thread through device manager.
- Click on Start Menu.
- Click on “Settings”.
- Click on “Device”.
- Go to “Printers and scanners or connected devices” and select the “Device Manager” option.
- Expand the “Processors” tab, and the number of CPU threads will appear.
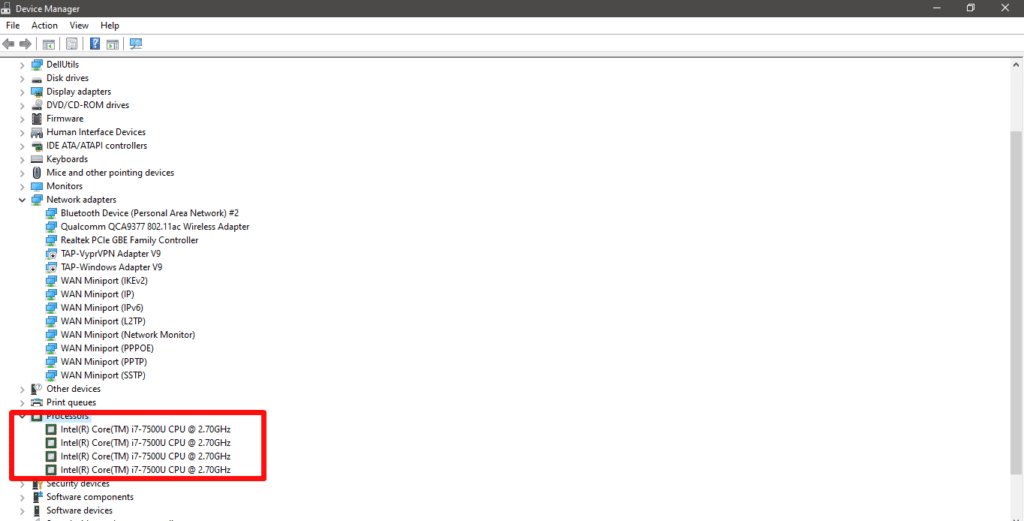
Method #3: Checking Windows System Information
It is possible to check the CPU threads with the Windows System Information tab by performing the following steps.
- Search for “System Information” on the search bar and click to open it.
- Search for “Processor” in the search menu below.
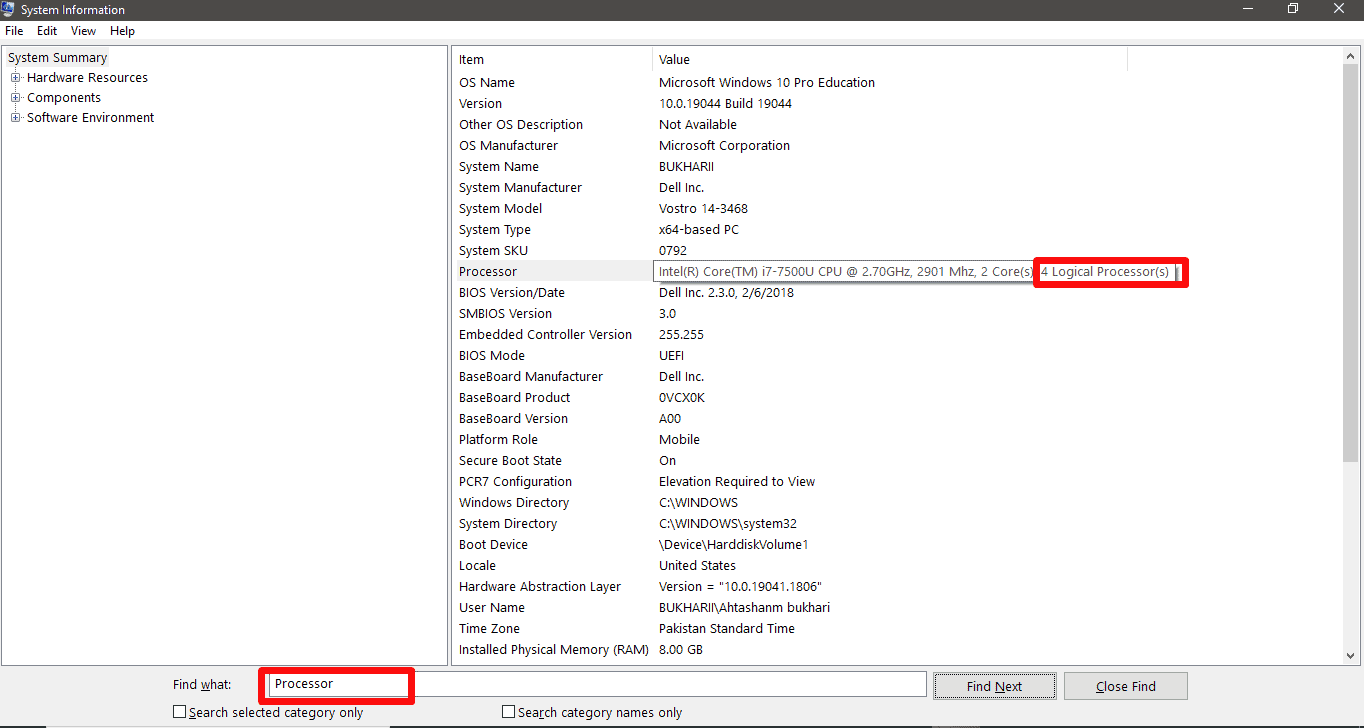
Move the cursor over the “Processor” option in the right pane, and see the number of CPU threads installed on your system.
Method #4: Checking with Third-Party Software
Another quick way to check CPU threads is to use third-party software such as CPU-Z. After downloading and installing the software, it will display every detail about the system including the CPU.
Although this software is usually designed for advanced users, you can extract the required information with a little practice.
- Press the keyboard shortcuts (Windows Key + X) and click “Windows Power Shell (Admin)” to open it from the menu.
- Type WMIC CPU Get NumberOfCores in the command line and press Enter.
- The number of CPU threads and cores will be displayed on the window.
- From the number of cores, estimate the number of threads. For example, 2 cores/4 threads.
Method #6: Using Command Prompt
You can also check CPU threads in two ways using Command Prompt and Windows Management Instrumentation.
Way #1: Using WMIC
- Press the keyboard shortcut (Windows Key + R), and the Run dialog box will open.
- Type wmic and press “OK”.
- Type cpu get numberofLogicalProcessors at the Windows Management Instrumentation command prompt.
- Press Enter, and the number of threads in the CPU will be displayed.
Way #2: Using Command Prompt
Press the keyboard shortcuts (Windows Key + S).
Type cmd.
Press Enter.
Type wmic cpu get numberofLogical Processor in the command prompt, and the number of logical processors will show CPU threads.
What Is Multithreading?
Typically, a single CPU core has at least one thread. However, for better system performance, the number of virtual cores (threads) often exceeds the number of physical cores, which is called multithreading.
To check if multithreading is enabled on your system, press the Window + S keys on the keyboard to open a command prompt, type CPU get numberofcores, numberofLogicalProcessors/Format:List, and press Enter. If the number of logical processors is equal to the number of cores, the CPU is not multithreaded.
Moreover, you can also enable or disable multi-threading on your system. However, the more threads your CPU has, the better and faster it can run and execute multiple programs in parallel.
Moreover, you can also enable or disable multi-threading on your system. However, the more threads your CPU has, the better and faster it can run and execute multiple programs in parallel.
Final Thought
This comprehensive guide discusses checking CPU threads using Task Manager, Device Manager, System Information, and other methods with simple instructions.
Hope your query is resolved, and now you can easily check your processor performance and increase it by viewing the information and closing the resource-hungry tasks on your computer.